云南大学中国西南天文研究所研究团队发布首个南天银河系三维星际尘埃分布图
A three-dimensional extinction map for the southern sky
星际尘埃主要产生于恒星演化晚期,它们是银河系的重要组成部分,在星系演化、恒星与行星系统的形成,乃至生命的起源中都起着重要作用。此外,星际尘埃会吸收和散射可见光与近红外波段的光线,产生消光与红化效应,所以依赖这些观测的科学研究必须考虑去除星际尘埃的影响。天文学家通过制定精确的银河系三维尘埃消光分布图,以准确地改正观测天体的消光与红化效应;并进一步测量银河系的尘埃结构参数,以研究银河系的结构、形成与演化历史。由于国内外大多数巡天望远镜都是位于北天,当前大部分的光学和近红外天文巡天观测都覆盖的是北天可观测天区,所以目前国际上还缺乏一个针对南天天区的银河系三维尘埃消光分布图,且对整个银河系的尘埃分布结构还缺乏一个准确的估计。
近日,云南大学中国西南天文研究所研究团队基于SkyMapper南天巡天(SMSS)第一版数据,结合2MASS、WISE以及Gaia巡天测光数据,测量了银河系超过1900万颗恒星的消光值,获得了国际上首个覆盖南天约1.4万平方度的银河系三维尘埃消光分布图。该消光图在银纬−10 deg < b < 10 deg, −30 deg < b < −10 deg及 b < −30 deg区域的角分辨率分别为6.9, 13.7和27.5角分。单颗星E(B−V)的典型误差为0.07mag,三维消光图E(B−V)的典型误差为0.03mag。基于此消光图,再结合文献中的数据,研究团组构建了一张覆盖全天的银河系三维尘埃消光图,并研究了银河系尘埃的结构参数。结果显示,银河系的尘埃盘更倾向于由一个尘埃“薄”盘和一个尘埃“厚”盘组成,对应的标高分别为73 pc和225 pc。
这项工作已被国际天文学主流期刊《天体物理学报》(ApJ)接受发表,预印本链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.14092 。论文第一作者是研究所博士生郭贺龙,指导老师为陈丙秋副教授和刘晓为教授。
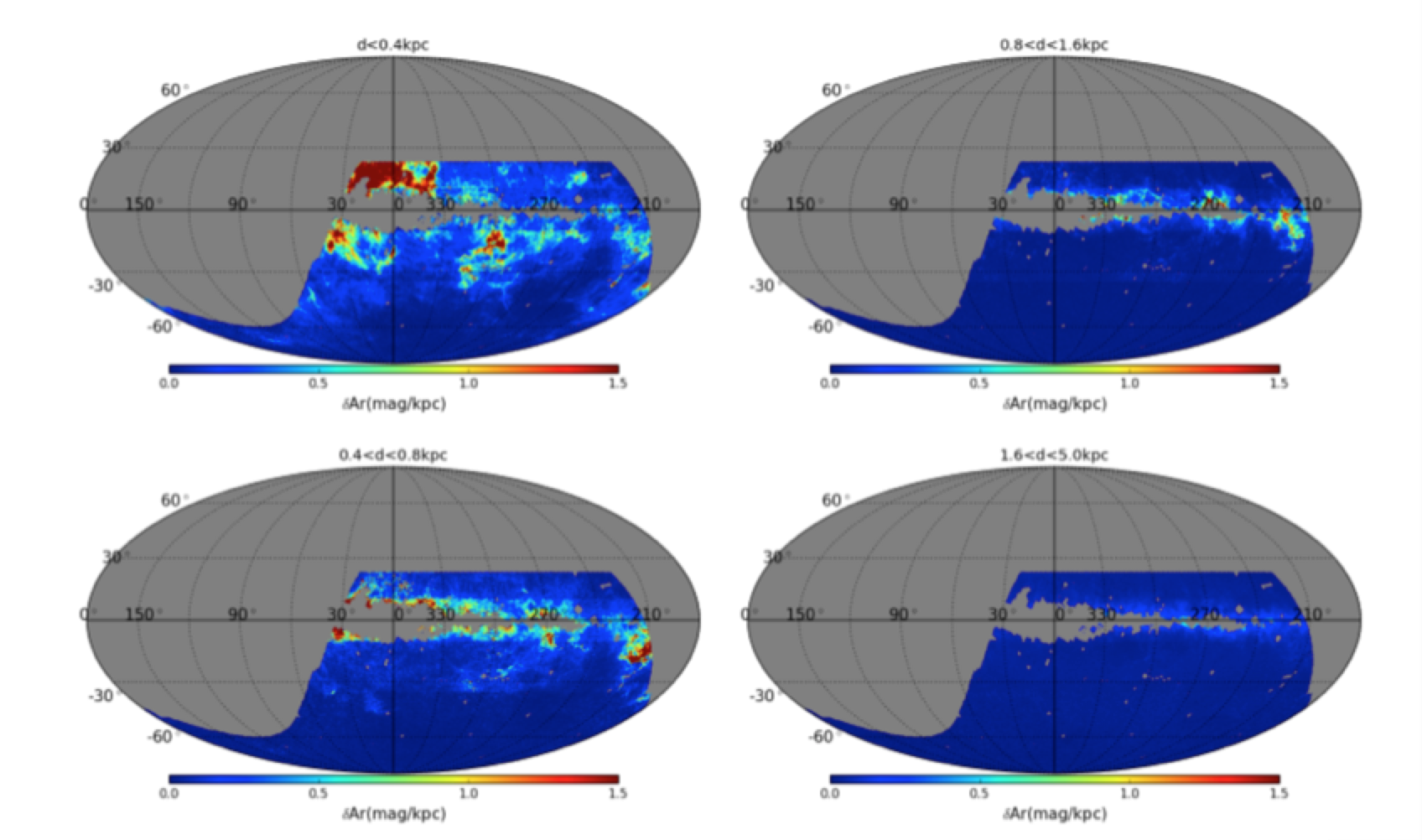
图1:不同距离区间的南天银河系尘埃消光分布图, 灰色阴影区域是未覆盖的区域。 Distributions of r-band extinction in the individual distance bins. Regions shaded grey are areas not covered by the current map.

Extinction and reddening by the interstellar dust grains pose a serious obstacle for the study of the structure and stellar populations of the Milky Way galaxy. In order to obtain the intrinsic luminosities or colors of the observed objects, one needs to correct for the dust extinction and reddening. Extinction maps are useful tools for this purpose. Since most of the recently completed large-scale surveys targeted the northern hemisphere, essentially all the currently available 3D extinction maps covered only the northern sky. A 3D extinction map for the southern hemisphere is still missing and should be of great value to, for example, explore the global dust distribution and the structure of the Milky Way.
Based on the multi-band photometry from the SMSS DR1, 2MASS, WISE and Gaia surveys, we have estimated values of r-band extinction for over19 million stars and constructed a 3D extinction map of the southern sky, covering the SMSS survey area of ~14,000 sq.deg. The map has an angular resolution of 6.9 arcmin for Galactic latitude −10 deg < b < 10 deg, 13.7 arcmin for −30 deg < b < −10 deg, and 27.5 arcmin for b < −30 deg. The typical error of E(B−V) for a single star is 0.07 mag, and that of the 3D extinction map is 0.03 mag.
By combining our 3D extinction map with those from the literature, we present an all-sky 3D extinction map, and use it to explore the 3D distribution of Galactic dust grains. We find that the data are best fitted with a model of two disks, a “thin” and a “thick” disk of scale height 73 and 225 pc, respectively.
The work has been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal (ApJ). The leading author of the paper, Mr. Helong Guo, is an PhD student of SWIFAR under the supervision of Profs. Bingqiu Chen and Xiaowei Liu (https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.14092 ).
